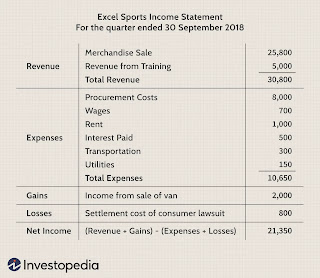
Income statement
- Primarily focuses on the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period
- Also known as the profit and loss statement or the statement of revenue and expense
- Structure: Focuses on four key items—revenue, expenses, gains, and losses
- Net Income = (Total Revenue + Gains) – (Total Expenses + Losses)
- Revenues and Gains
- Operating revenues
- i.e., revenue achieved from the sale of the product
- Non-operating revenues
- e.g., revenue from interest, rental income from business property, income from strategic partnerships like royalty payment receipts, etc
- Gains
- e.g., the net income realized from one-time non-business activities, like a company selling its old transportation van, unused land, or a subsidiary company
- Expenses and Losses
- Primary activity expenses
- e.g., the cost of goods sold (COGS), selling, general and administrative expenses (SG&A), depreciation or amortization, and research and development (R&D) expenses
- Secondary activity expenses
- e.g., interest paid on loan money
- Losses as expenses
- e.g., one-time or any other unusual costs, or expenses towards lawsuits


No comments:
Post a Comment