5G
- The fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019
- c.f., broadband
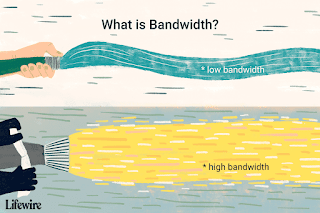
- Wide bandwidth data transmission which transports multiple signals and traffic types.
- The medium can be coaxial cable, optical fiber, radio or twisted pair.
- c.f., cellular network (or mobile network)
- a communication network where the last link is wireless
- The network is distributed over land areas called "cells", each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver
- Capacity
- 5G can support up to a million devices per square kilometer, while 4G supports only up to 100,000 devices per square kilometer
- Speed
- The main advantage of the new networks is that they will have greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds, eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s)
- Use
- Due to the increased bandwidth, it is expected the networks will not exclusively serve cellphones like existing cellular networks, but also be used as general internet service providers for laptops and desktop computers, competing with existing ISPs such as cable internet, and also will make possible new applications in internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine areas.
- Three frequency bands
- The increased speed is achieved partly by using higher-frequency radio waves than previous cellular networks.
- However, higher-frequency radio waves have a shorter useful physical range, requiring smaller geographic cells.
- For wide service, 5G networks operate on up to three frequency bands — low, medium, and high
- The first mobile phone
- Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, the first smartphone able to connect to 5G networks




No comments:
Post a Comment